Building High-Performance Organizations from the Ground Up: The HR Strategy Pyramid
- Jennifer Azapian
- Feb 12, 2025
- 5 min read
Updated: Jul 23, 2025

Winning Business Strategy + Funding + Effective Talent Strategy =
Competitive Advantage
Especially in the startup context, this fundamental equation drives sustainable success. Yet many emerging companies struggle to execute on each element simultaneously, often prioritizing business strategy and fundraising at the expense of talent strategy, or the reverse – hiring top talent without a coherent business strategy or a funding runway that’s responsive to the company’s stage or the market it’s selling to.
In the first case, sustainable team growth and development will hit speed bumps as the business scales rapidly, causing lack of coordination, dysfunction and/or excessive headcount turnover.
In the second case, experienced management hired without an appropriate understanding of company maturity or growth trajectory – and without establishment of a coherent people vision or leadership values - can end up implementing mature-company systems and processes before the business is prepared for that level of management delegation and complexity.
Drawing on my experience working with high-growth companies, I've developed a simple visual framework to guide this conversation.
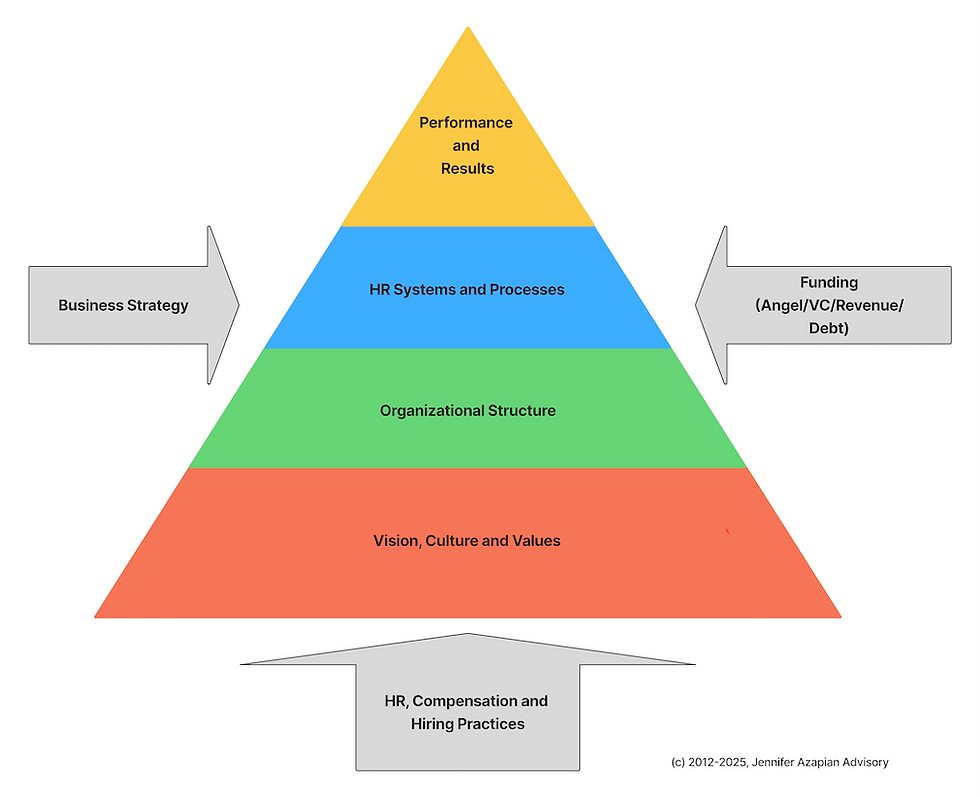
This graphic depicts how three primary forces shape strategic talent initiatives while emphasizing the building blocks that support performance and results. Let's explore how each component contributes to building lasting competitive advantage.
Three Key Forces: The Shapers of HR Strategy
Three primary forces constantly influence and shape the HR Strategy pyramid:
1. Business Strategy
Market dynamics and competitive landscape evolution
Growth trajectories aligned with funding stages
Product-market fit iterations and pricing strategy
Customer acquisition and retention patterns
2. Funding
Angel/Seed Funding: Requires focus on establishing core cultural elements and key founding team with execution capabilities
Venture Capital: Often involves significant pressure for rapid growth and necessitates competitive compensation strategies
Revenue-Funded Growth: Emphasizes sustainable scaling and efficient resource utilization
Debt Financing: Requires careful management of fixed costs, with focus on revenue-generating roles
3. HR, Compensation & Hiring Practices
Recruitment quality, talent market dynamics and skills availability
Compensation philosophy, industry compensation benchmarks and competitive practices trends
Remote work, distributed/hybrid, outsource/offshore, and in-office team strategy
HR policies and team
Four Strategic HR Tiers: The Infrastructure
Foundation: Vision, Culture, and Values
The base of the pyramid represents the bedrock of any successful organization. In the startup context, this foundation is particularly crucial as it guides decision-making during periods of rapid growth and uncertainty, and can create coherence in a team and between cofounders when results aren’t yet happening.
Experienced Operators and VC’s and as well as research from leading academics consistently show that startups with clearly articulated culture, vision and values demonstrate superior cofounder and team alignment, scaling, and execution capability.
Key considerations for startups and scaleups:
Vision must be both ambitious and actionable, serving as a north star for strategic decisions
Culture should be intentionally designed through systematic processes, not left to emerge organically.
Values need to be specific enough to drive behavioral expectations and inform performance evaluation frameworks
The benefits of this are multiple:
1. Consistent Leadership/Management style
2. Clear Hiring guidelines
3. Differentiated values lead to self-selection (desiring or rejecting a specific work style, affiliation, & professional identity) by potential candidates
4. Establishes Norms for communication, work style, and taking action
Structural Integrity: Organizational Design
The second layer focuses on creating an organizational structure that enables rapid scaling while maintaining operational efficiency. Unlike traditional corporate hierarchies, startup structures need to be fluid and adaptable while providing enough framework to prevent chaos. This is where many startups beginning to scale face their first major growing pains.
Essential elements:
Clear reporting relationships that preserve autonomy while ensuring accountability
Role definitions that emphasize responsibilities and outcomes over tasks, allowing for rapid evolution
Team structures that promote cross-functional collaboration, limited hierarchy, and rapid innovation cycles
Understanding what roles/people can develop into team managers vs. senior IC’s
Operational Excellence: HR Systems and Processes
As startups scale, the HR systems and processes layer becomes increasingly critical. This layer transforms good intentions into repeatable actions, ensuring consistency without bureaucracy overkill. Leading venture capital firms cite operational scalability as a key indicator of investment readiness – and that scalability and adaptability includes having HR systems in place to effectively hire, onboard talent, and scale your company.
Focus areas:
Talent acquisition that prioritizes cultural synch and talent growth potential along with cost-effective compensation
Recruitment is priority for hiring managers; consistent interview methodology
Compensation policies and practices that are consistent and fair, with some flexibility for special cases
Performance management tools and frameworks that balance accountability with development
Learning and development investments tied directly to business outcomes
Communication protocols that scale effectively across distributed or hybrid/remote/in person teams
HR data and compliance practices that are straightforward, efficient and accurate
Summit: Performance and Results
The apex of the pyramid represents the ultimate goal: exceptional organizational performance. This encompasses not just financial metrics, but also operational speed and excellence, innovation output, and team engagement. High-performing startups consistently show strong alignment between individual, team, and business performance metrics, frequently measured with OKR’s.
Measuring success:
Key performance indicators (KPI’s/OKR’s) directly linked to value creation
Employee engagement metrics that predict retention and productivity
Innovation metrics that track both output and impact
Team velocity and adaptation capabilities
Alignment and cultural assessment
Practical Implementation for Startups
Start with a Strong Foundation
Document your vision, culture, and values through collaborative exercises
Involve early team members in cultural development to ensure buy-in
Establish regular culture health checks and adjustment mechanisms
Build Flexible Structures
Design roles around responsibility, outcomes and value creation
Create career progression frameworks that support rapid growth and increasing scope
Maintain structural flexibility while establishing clear decision accountability
Implement Essential Systems Early
Choose scalable HR technology and services solutions that grow with your organization
Document core processes while preserving agility
Regular audits and reviews focused on reporting and financial/compliance process efficiency and strategic effectiveness
Focus on Leading Indicators
Define success metrics that predict rather than just retrospectively measure performance. Measure what matters.
Implement continuous feedback loops at all organizational levels
Regular strategic alignment checks between team, leadership, and business objectives
The HR Strategy Pyramid provides a high-level framework for building and scaling organizations. These layers build upon each other both sequentially and synergistically. In the startup context, where speed and adaptability are crucial, this framework helps leaders make informed decisions about their people and organizational development initiatives, and stand on solid ground when discussing these initiatives with investors and board members.
Remember: your HR strategy isn't just a component of your business strategy—it's a crucial multiplier of your competitive advantage. The most successful startups are those that master all of the elements of our opening equation, creating sustainable, adaptable competitive advantage through the deliberate development of their organizational capabilities.



